In vitro inhibition of multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas efflux pump by Xylopia aethiopica (Dunal) A. Rich
AROC in Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology, 2021, 1(2);20-27
- Author(s): Jeremiah John Oloche, Bolaji Bosede Oluremi and Temiloluwa Oyindamola Koya
- September 14, 2021
- eISSN - 2789-3928
- Keywords - P. aeruginosa; Modulation factor; Xylopia aethiopica; Zones of Inhibition; Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
Abstract
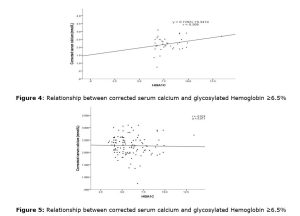
Global health is under constant threat due to antimicrobial drug resistance. Bacterial Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa are of importance because of their antibiotics resistance. This study aimed at evaluating the effects of extracts of Xylopia aethiopica (XA) on multidrug-resistant (MDR) Pseudomonas isolates. Fresh samples of XA leaf, stem bark and roots were collected from the botanical garden, University of Ibadan, Nigeria. Dried and pulverized samples were extracted with methanol and partitioned into n-hexane, dichloromethane and ethyl acetate. Phytochemical screening of the extracts was performed by standard methods. Antimicrobial activity and synergistic interaction were determined using microdilution and checkerboard broth dilution methods, respectively. The results revealed that crude methanol extracts of XA leaf, stem bark and root significantly (p0.05) compared with ciprofloxacin/verapamil combination. In conclusion, the root and leaf fractions Xylopia aethiopica that demonstrated antimicrobial activity against MDR P. aeruginosa and synergised with ciprofloxacin have the potential to rejuvenate the antimicrobial activity of ciprofloxacin in MDR P. aeruginosa.
Corresponding Author(s)
Bolaji Bosede Oluremi;
Email: bolaji0708@gmail.com
Citations
Oloche, J.J., Oluremi, B.B., and Koya, T.O. (2021). In vitro inhibition of multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas efflux pump by Xylopia aethiopica (Dunal) A. Rich. AROC in Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology, 1(2);20-27, https://doi.org/10.53858/arocpb01022027