Mexicanolide, a bioactive compound from Cedrela odorata: In silico study of its pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness, potential drug targets, and cytotoxic activities against cancer cell lines
BIOMED Natural and Applied Science, 2021,1(2):1-10
- Author(s): Blessing U. Alozieuwa, Shehu U. Abdullahi, Abdulhakeem R. Agboola, Bernard O. Odey, Adaaja B. Ovaiyoza, Otiwa G. Iyaji, Zaman E. Yuyu, Oloyede E. Olayinka, Dauda Muhammed and Eustace B. Berinyuy
- July 29, 2021
- eISSN - 2789-178X
- Keywords - Mexicanolide, Cedrela odorata; in silico study; pharmacokinetics; drug-likeness; drug targets; cytotoxity; cancer cell lines
Abstract
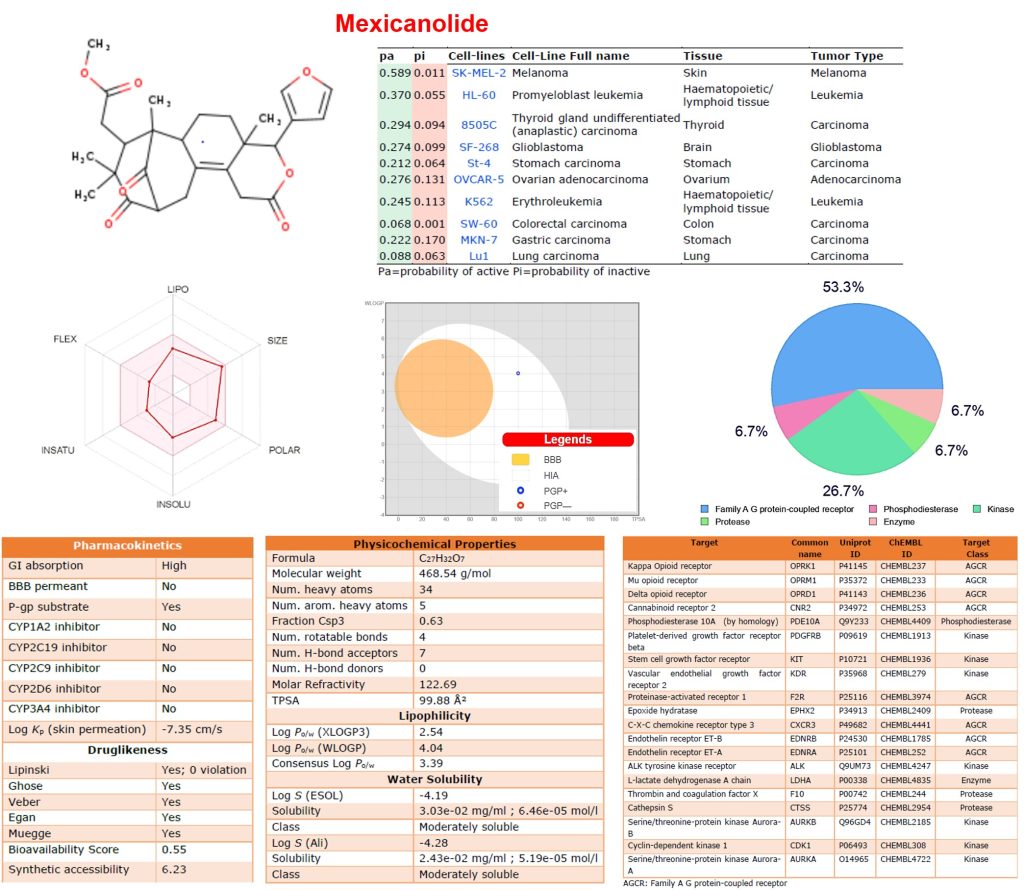
Mexicanolide is a limonoids type of compound identified from Cedrela odorata, a forest plant with various medicinal properties. Several biological activities have been reported for Mexicanolide. In the present study, we used an in silico approach to evaluate the physicochemical, pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness, drug targets, and cytotoxic activities of mexicanolide from Cedrela odorata. The results revealed that mexicanolide has favorable physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties of a good drug-like candidate. Notably, the compound has a high GI absorption rate but could not permeate the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and has poor synthetic accessibility. Several proteins targets including Kappa Opioid receptor, Mu opioid receptor, delta-opioid receptor, Cannabinoid receptor 2, Phosphodiesterase 10A (by homology), Platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta, Stem cell growth factor receptor, Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, Proteinase-activated receptor 1, and Epoxide hydratase were identified as target candidates for mexicanolide. Furthermore, mexicanolide demonstrated in silico activities against several types of cancer cell lines including the SK-MEL-2, HL-60, 8505C, SF-268, St-4, OVCAR-5, K562, SW-60, MKN-7, and Lu1. In conclusion, mexicanolide has favorable physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties of a good drug-like candidate and could be considered a multi-target compound with potential anticancer activities
Corresponding Author(s)
Blessing U. Alozieuwa
E-mail:alozieuwau@veritas.edu.ng
Citations
Alozieuwa, B.U., Abdullahi, S.U., Agboola, A.R., Odey, B.O., Ovaiyoza, A.B., Iyaji, O.G., Yuyu, Z.E., Olayinka, O.E., Muhammed D., and Berinyuy, E.B. (2021). Mexicanolide, a bioactive compound from Cedrela odorata: In silico study of its pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness, potential drug targets, and cytotoxic activities against cancer cell lines. BIOMED Natural and Applied Science,1(2):1-10, https://doi.org/10.53858/bnas01020110