Nutritional evaluation of the peels from Citrullus lanatus and Manihot esculenta, an insight into the conversion of waste to food
AROC in Food and Nutrition, 2021, 1(1);1-7,
- Author(s): Tsado A. Ndarubu, Gana David, Ibrahim A. Habiba, Jiya A. Gboke, Zubairu Rakiya, Okoli N. Rosemary, Danazumi Nathaniel
- May 24, 2021
- Keywords - Proximate; minerals; amino acid; cassava peels; watermelon peels
Abstract
Background: Huge quantity of cassava and watermelon wastes are daily discharged to the environment with unwholesome consequences. Therefore, research into the effective utilization of these agricultural by-products is of global interest.
Methods: The present study evaluated the proximate, minerals, and amino acid compositions of cassava and watermelon peels using standard procedures.
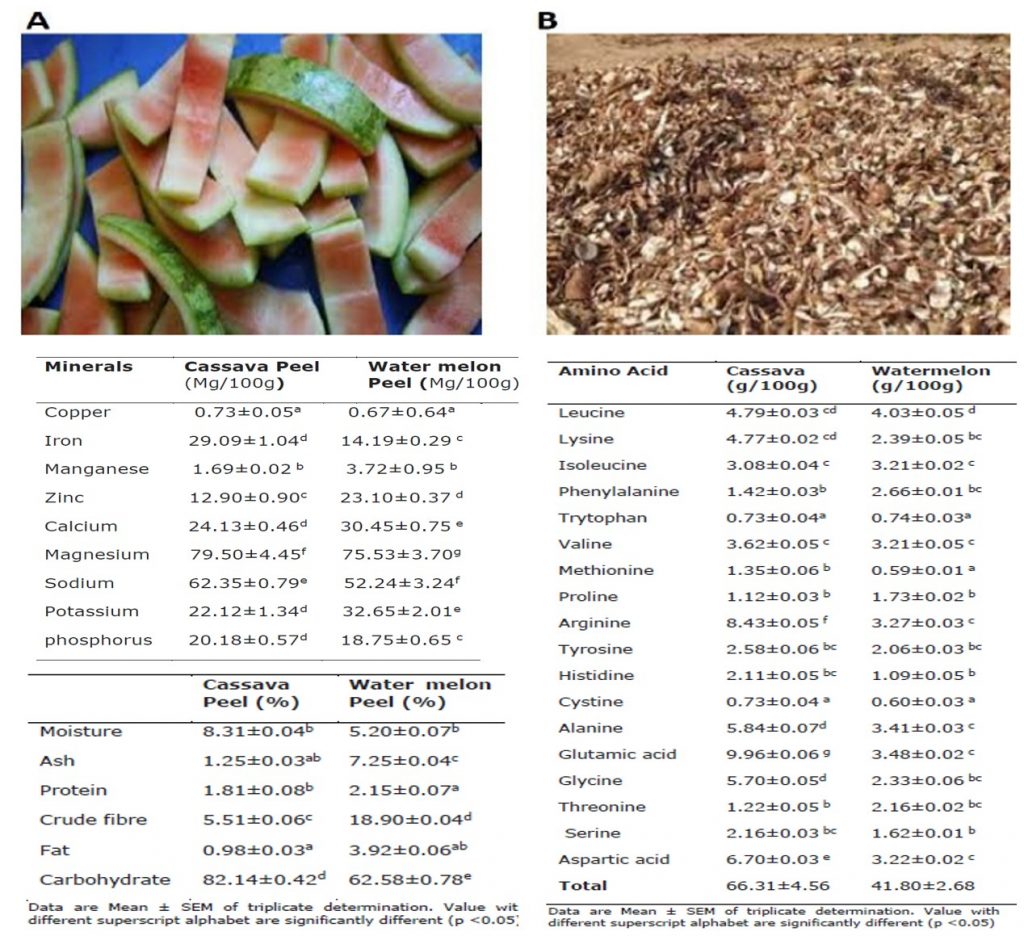
Results: The results revealed that carbohydrate is the most abundant proximate contents of both the cassava (82.14±0.42%) and watermelon (62.58±0.78%) peel, followed by crude fiber (5.51±0.06% and 18.90±0.04%), moisture (8.31±0.04% and 5.20±0.07%), crude ash (1.25±0.03% and 7.25±0.04%) for cassava and watermelon peels respectively, while crude fat (0.98±0.03% and 3.92±0.06%) is the least abundant proximate in both samples. Magnesium is the most abundant mineral contents of both the cassava (79.50±4.45Mg/100g) and watermelon (75.53±3.70Mg/100g) peel, followed by sodium (62.35±0.79 Mg/100g and 52.24±3.24 Mg/100g), potassium (22.12±1.34 and 32.65±2.01 mg/100g) for cassava and watermelon peels respectively while copper (0.73±0.05 Mg/100g and 0.67±0.64 Mg/100g) was the least abundant minerals in both samples. The total amino acid compositions of 66.31±4.56 g/100g and 41.80±2.68 g/100g were recorded for cassava and watermelon peel. Glutamic acid (9.96±0.06g/100g) and leucine (4.03±0.05 mg/100g) the most abundant amino acid in cassava and watermelon seed respectively.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the peels of cassava and watermelon examined, have appreciable levels of nutrients compositions that can be incorporated into human and animal feed formulation.
Corresponding Author(s)
*Correspondence:
Tsado A. Ndarubu
infoamosndarubu@gmail.com
Mobile-+2348032920909
Citations
Citation: Tsado, A.N., Gana, D., Ibrahim, A.H., Jiya, A.G., Zubairu, R., Okoli N.R., and Danazumi N. (2021). Nutritional evaluation of the peels from Citrullus lanatus and Manihot esculenta, an insight into the conversion of waste to food. AROC in Food and Nutrition, 01(01);01-07, https://doi.org/10.53858/arocfn01010107