1.0 Introduction
In all biomedical applications today, polymers are playing an important role. Many notable advances in technology have followed exploitation of the properties offered by new polymeric materials like blends and composites [1,2]. Biopolymers include the polysaccharides such as cellulose, starch, the carbohydrate polymers produced by bacteria and fungi and animal protein-based biopolymers such as chitin, chitosan, wool, silk, gelatin and collagen, Biopolymers, especially the carbohydrate origin, have been found to have a very promising industrial application in various forms [3,4]. Most commercial polysaccharides (e.g., cellulose, dextran, pectin, alginic acid, agar–agar, agarose, starch, carrageenan, and heparin) are either neutral or acidic, but chitosan is a basic polysaccharide [5].
Chitosan is a copolymer that consists of β-(1 → 4)-linked 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D glucopyranose and 2-amino-2-deoxy-Dglucopyranose units [5]. This is generally obtained by alkaline deacetylation of chitin, which is the main component of the exoskeleton of crustaceans, such as shrimps, prawns, crabs, krills squids, crayfish, lobsters e.t.c [6]. Chitin is a naturally abundant mucopolysaccharide and is second to cellulose in terms of the amount produced annually by biosynthesis. The structure of chitosan (deacetylated chitin) is very similar to cellulose [7]; however, less attention has been paid to chitin than cellulose, primarily due to its inertness. Hence, it remains an essentially unutilized resource [8]. Deacetylation of chitin yields chitosan, which is a relatively reactive compound and is produced in numerous forms, such as powder, paste, film and fibre [9].
Chitosan is soluble in dilute aqueous acetic, lactic, malic, formic and succinic acids[10]. Chitosan is polycationic at pH < 6 and it readily interacts with negatively charged molecules, such as proteins, anionic polysaccharides (e.g., alginate and carrageenan), fatty acids, bile acids and phospholipids [11]. Nonetheless, chitosan may also selectively chelate metal ions such as iron, copper, cadmium and magnesium [10]. Much attention has been paid to chitosan-based biomedical materials, because of its unique properties such as biodegradability, non-toxicity, anti-bacterial effect and biocompatibility [12].
Chitosan can be found in nature in the cell wall of fungi (of the class Zygomycetes), mushrooms and in insect cuticles. Generally, chitin is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods (crustaceans, insects, myriapods and arachnids) [13]. The natural biopolymer occurs naturally in three polymorphic forms with different orientation of the microfibrils known as alpha (α), beta (β)and gamma (γ) chitin [14]. Chitin and chitosan have excellent properties, such as biodegradability, biocompatibility, no toxicity and absorption [15]. Chitin and chitosan are now attracting great interest because of their wide range of potential applications in the field of biotechnology, medicine and pharmacology, agriculture, textiles, cosmetics and wastewater treatments [10,16]
Chitosan has a number of commercial and possible biomedical uses. It can be used in agriculture as a seed treatment and biopesticide, helping plants to fight off fungal infections [17]. In winemaking, it can be used as a fining agent, also helping to prevent spoilage. In industry, it can be used in a self-healing polyurethane coating [14]. In medicine, it is useful in bandages to reduce bleeding and as an antibacterial agent; it can also be used to help deliver drugs through the skin [18]. More controversially, chitosan has been asserted to have used in limiting fat absorption, which would make it useful for dieting, but there is evidence against this [13]. Other uses of chitosan that have been researched include use as a soluble dietary fibre [19]. This study was designed specifically to explore locally available chitosan from cockroach and cricket as an alternative source of chitosan, chemically characterizing the extracted chitosan using FTIR spectroscopy, GCMS, SEM analysis, Degree of deacetylation and Percentage Solubility.
2.0 Materials and methods
2.1 Collection and identification of insects
The Acheta domisticus and Periplaneta americana were collected from Bosso area, behind Federal University of Technology, Minna. Nigeria They were taken to the Department of animal biology for authentication by two independent Entomologist. The body of the insects were rubbed with 80-85% alcohol to preserve the body from drying, decaying and breaking into pieces. Then stored in a big jar that has an air tight lid until required.
2.2 Preparation of the extract
The insects were sorted into cockroach and cricket species and their exoskeleton were prepared for the study by first removing the internal organs and scraping any loosed tissue. The materials were then washed, dried and crushed into powder using mortar and pestle.
2.3 Isolation of chitin and synthesis of Chitosan
The isolation of chitin and synthesis of chitosan from Acheta domisticus and Periplaneta americana was carried out as described in previous studies [16] [20-22]. The exoskeleton does not exist as standalone biopolymer, but rather in a conglomeration with other biomaterials, mainly proteins, lipids and inorganic salt. In the process, treatment of the exoskeleton with 5% HCl dissolves the calcium salts and lipids and other minor inorganic constituents to yield chitin. Treating the resultant chitin with 40% NaOH solution at 120°Cfor 2 hours with stirring for homogeneity, yielded the desired chitosan [16] [20]. During the alkaline treatment, a concomitant hydrolysis of the acetamido groups of chitin takes place, this results in the formation of Chitosan. The resultant chitosan were washed thoroughly with distilled water and oven dried at 50 °C for 24 hours [21,22].
2.4 Purification of the chitosan
The extracts were purified by dissolving in 2% acetic acid and re precipitated out using 20% NaOH solution. The pure chitosan was then washed to neutrality and oven dried for 24 hours and then grounded into powder with an electrical blender. The process of deacetylation of chitin to chitosan were confirmed using the method described previously [23]. Briefly, 5ml of I2 / KI solution was added to each testube which gives a yellow colouration to the solution. To this solution concentrated sulphuric acid was added, the colour changes from yellow/brown to dark purple indicated the presence of chitosan.
2.5 Characterization of chitosan
2.5.1 Fourier Transformed Infra-Red Spectroscopy (FTIR)
The FTIR spectra of chitosan was measured with Shimadzu FTIR Spectrophotometer. The spectra was average scan of 45 scans recorded at resolution of 16 (1/cm) in the range of 4000– 500cm-1 spectral region. The absorbance of the spectral peak observed was compared with the absorbance of the reference peak to determine the degree of deacetylation of the sample [22].
2.5.2 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Scanning electron microscope Quanta 200, FEGESEM was used to examine the surface morphology of the chitosan powder from the Periplaneta americana and Acheta domesticus.
2.5.3 Degree of deacetylation
The degree of deacetylation (DD) of chitosan obtained from cockroach and cricket were determined by comparing the absorbance of the Amide peak to that of the hydroxyl group. This was used to calculate the degree of deacetylation of the samples using formular below
DD = 100 – [A1659 / A3428 * 100/1.33
Where A1659 and A3428, are the absolute heights of the absorption bands of Amide and Hydroxyl groups respectively and 1.33 is a constant [24]
2.5.4 Solubility of chitosan
The chitosan samples from cockroach and cricket were tested for solubility in aqueous solution of acetic acid. One gram of chitosan powder from the cockroach and cricket was weighted and labeled as A and B for each chitosan in a centrifuge tube (of known weight) respectively and dissolved with 10ml of 10% acetic acid solution for 30minutes using an incubator shaker at 240rpm and 25°C. The solution was then immersed in boiling water bath for10minutes, cooled to room temperature and then centrifuged at 10,000rmp for 10 minutes. The supernatants were decanted and the un dissolved particles were washed in distilled water and then centrifuged at 10,000rmp and the supernatant was removed and the undissolved particles were dried at 60°C for24hrs: finally, weight and the percentage solubility were calculated [24].
2.5.5 Gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC-MS)
The GC-MS analysis was carried out on a GC-MS (Model: QP2010 PLUS Shimadzu, Japan) comprising a AOC-20i auto-sampler and gas chromatograph interfaced to a mass spectrometer (GC-MS) The instrument is equipped with a VF 5 ms fused silica capillary column of 30 m length, 0.25 mm diameter and 0.25 μm film thickness. The temperatures employed were; column oven temperature 80ºC, Injection Temp 250ºC at a pressure of 108.0 kPa, with total flow and column flow of 6.20 ml/min and 1.58 ml/min respectively. The linear velocity was 46.3 cm/sec and a purge flow of 3.0 ml/min. The GC program ion source and interface temperature were 200.00ºC and 250.00ºC respectively with solvent cut time of 2.50 min. The MS program starting time was 3.00min which ended at 30.00 min. with event time of 0.50 sec, scan speed of 1666 μl/sec, scan range 40-800u and an injection volume of 1 μl of the plant extract (split ratio 10:1). The total running time of GC-MS was 30 min. The relative percentage of the extract was expressed as percentage with peak area normalization [25] .
3.0 Results and Discussion
3.1 Chitosan yield from Periplaneta americana and Acheta domesticus
The yielding proportion of Chitosan obtained from Periplaneta americana and Acheta domesticus at various stages of extraction are depicted in Table 1. The extraction was initiated by demineralization process, where 10 and 15.77% of the samples were removed as minerals (comprising CaCO3 and other minor inorganic salts). This was followed by the deacetylation process in the presence of NaoH alkaline solution, at a very high temperature, yielding 55.39 % and 51.25 % of chitin to chitosan and 99.7 and 90.6% of the exoskeleton to chitosan from P. americana and A. domesticus respectively. The present study indicated that chitosan can be successfully extracted from Periplaneta americana (cockroach) and Acheta domesticus (cricket).
Kaya et al. [13] obtained a much lower yield when they worked on the chitosan from male and female grasshoppers, where they obtained the percentage yield as 36.4 % and 18.44 % respectively. This may be because they used 50 grams of exoskeleton which if increased could increase the yield. The work of Ladchumanadas et al. [26] got a similar result when they extracted chitosan from shrimp (396 g) and crabs (204 g). Even though crustaceans are bigger in size than cockroach and cricket (hence less amount of chitosan in the exoskeleton of the insects) the result of this study has shown that they are a good source of chitosan
Table 1: Percentage yield of Chitosan from Periplaneta americana and Acheta domesticus
| Category | Periplaneta americana | Acheta domesticus |
| Exoskeleton | 1000g | 1000g |
| Stage 1: % weight of the sample after demineralization | 900g (90%) | 884.23g (88.42% ) |
| Stage 2: weight of the product remaining after deacetylation | 498.52g (55.39%) | 453.2g (51.25% ) |
| weight of final product (chitosan) | 997.04g (99.7%) | 906g (90.6%) |
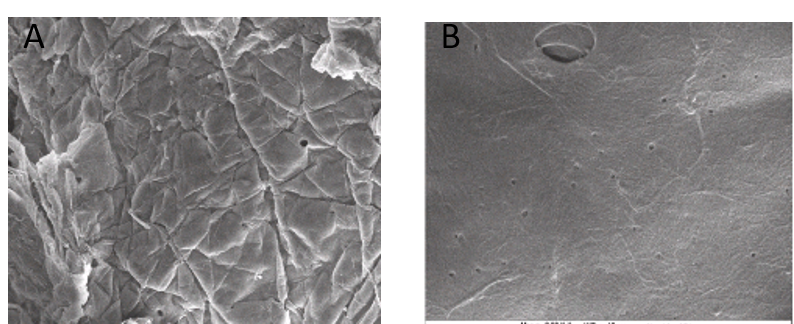
3.2 Scanning electron microscope profile of chitosan from P. americana and A.domesticus
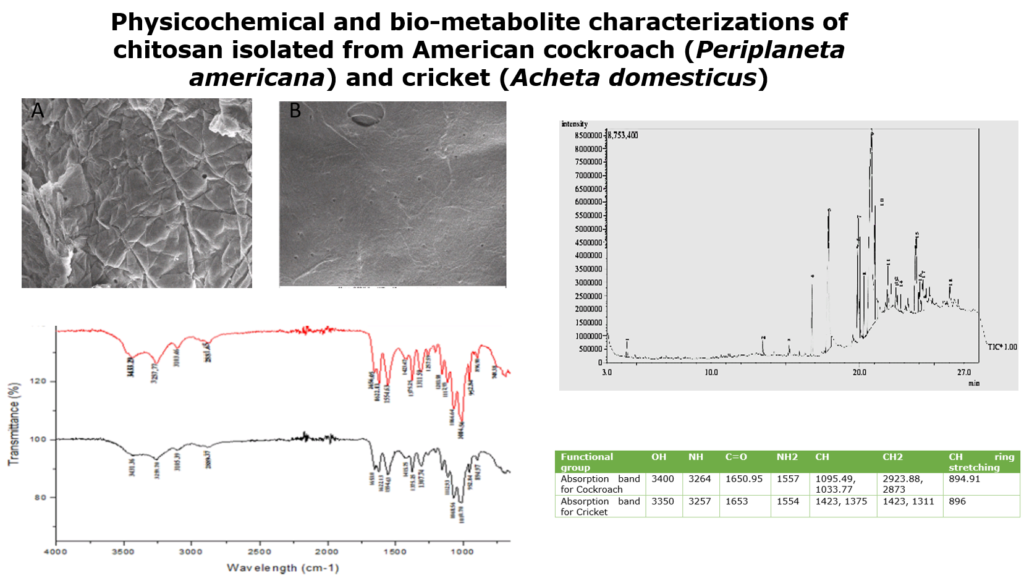
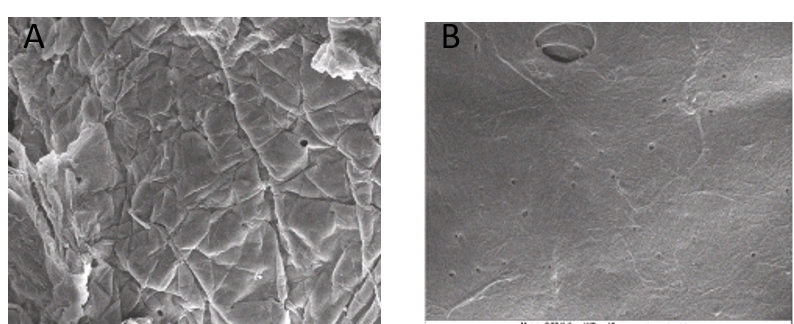
The morphology of Periplaneta americana and Acheta domesticus chitosan was studied by SEM micrograph at different magnifications (Figures 1 and 2). The chitin of P. americana had smooth surface with pores and fibrous veins on it. The chitosan had wrinkles on the surface, which might be as result of the same harsh conditions of deacetylation (Figures 1A and B). The general surface morphology of cricket chitosan presents a smooth surface with big pores that can be seen in some areas and fibres (figure 2). The surface morphology could be as a result of high protein content in the cricket which maintains the exoskeleton and makes it non porous.
The morphology of chitosan isolated from the insects, is similar to what was reported by Ibitoye et al. [22] and Chen et al. [27]; their work reported that chitin and chitosan had a combination of rough and smooth layers of flakes, also big pores can be seen in chitin and chitosan of both insects (cricket and cockroach).
3.3 FTIR profiles of chitosan from P. americana and A. domesticus
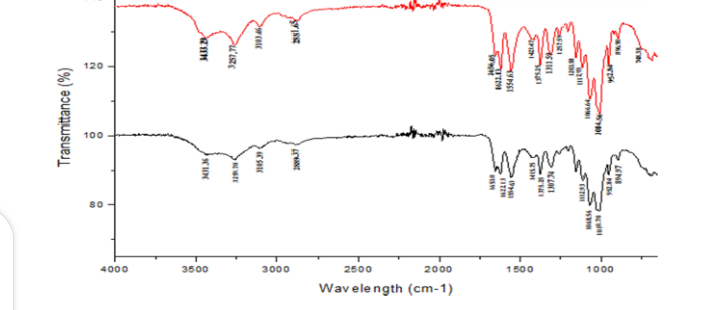
FTIR spectrum of Periplaneta americana and Acheta domesticus displayed the major characteristic band of chitosan as shown on Figure 3 and Table 2. The spectra showing a peak at 3400 cm-1 indicates symmetric stretching vibration of OH and amine absorption peak at 2923.88cm-1 indicates the presence of CH stretch which is characteristic of chitosan. Absorption band at 1650.95 was due to C=O stretching (amide I) 1095.49 and 1033.77 peaks for C-O stretching. NH bend, C=N stretching (amide II) at 1557 and NH stretching at 3284. Peak at 894.91 is a CH ring stretching a characteristic bond for glycosidic linkage which is also a characteristic of chitosan.
The work of Brugnerotto et al., [28]; Anicuta et al., [29] and Ibitoye et al., [22] reported similar result where they obtained amine absorption peak at 2923.88 cm-1, OH stretching at 3400,C=O stretching at 1650.95, 1033.77 and Peak at 894.91 (CH ring stretching, a characteristic bond for glycosidic linkage )when they carried out FTIR on cockroach chitosan. For the chitosan of A. domesticus, the spectra showing a peak at 3350 cm-1 indicates symmetric stretching vibration of OH and amine absorption peak at 1423cm-1 indicates the presence of CH stretch which is characteristic of chitosan. Absorption band at 1653 was due to C=O stretching (amide I) 1423 and 1375 peaks for C-O stretching. NH bend, C=N stretching (amide II) at 1554 and NH stretching at 3257. Peak at 896 is a CH ring stretching, a characteristic bond for glycosidic linkage which is also a characteristic of chitosan.
This results are in line with the study of Kovaleva et al., [30] who obtained a similar result when they carried out FTIR on the chitosan of cricket (C=O stretching (amide I) 1423 and 1375 peaks for C-O stretching. NH bend, C=N stretching (amide II) at 1554 and NH stretching at 3257. Peak at 896 is a CH ring stretching, a characteristic bond for glycosidic linkage).
Table 2: The FTIR absorption bands and chemical groups (cm-1) of chitosan in Cricket and Cockroach
| Functional group | OH | NH | C=O | NH2 | CH | CH2 | CH ring stretching |
| Absorption band for Cockroach | 3400 | 3264 | 1650.95 | 1557 | 1095.49, 1033.77 | 2923.88, 2873 | 894.91 |
| Absorption band for Cricket | 3350 | 3257 | 1653 | 1554 | 1423, 1375 | 1423, 1311 | 896 |
3.4 Degree of deacetylation of chitosan from Periplaneta americana and Acheta domesticus
The degree of deacetylation of the chitosan obtained from Periplaneta americana and Acheta domesticus have shown that P. americana had the highest yield and hence have high degree of deacetylation of 90.3 % while A. domesticus has 88.5%. This implies that the chitosan extracted from P. americana and A. domesticus has high degree of deacetylation and can be used as a source of chitosan.
A deacetylation degree of 55-70% is defined as a low deacetylated degree of chitosan, which is almost insoluble in water. Deacetylaytion degree of 70-85% is the middle deacetylation degree, which can partly dissolve in water. 85-95% is a high deacetylation degree of chitosan, which has good solubility in water, and 95-100% is called ultra-high deacetylation degree of chitosan, which is usually difficult to attain. Meanwhile, reducing the molecular weight of chitosan by degradation is beneficial to increasing its solubility in water [31].
Kaya et al. [13], reported a similar result when they worked on chitosan, obtained from male and female grasshopper and reported that male specie had the highest yield and had high degree of deacetylation of 98.63 %. While the female grasshopper has 89.43%. It was established that the degree of deacetylation (DD) of the chitosan extracted from male and female grasshopper are comparable (98-89%) and are higher than that of commercial chitosan from Shrimp, prawn, or crab [10,16]
3.5 Solubility of chitosan from Periplaneta americana and Acheta domesticus
It was established that P. americana chitosan was more soluble in dilute acetic acid with about 102.1% solubility, while A. domesticus chitosan had 93%. However, it was postulated that solubility below 87.0% is considered as low solubility [13]. From the results, it can be said that both insects had high solubility and therefore can be used conveniently as an alternative source of chitosan. The result is in conformity with Murat et al. [13] who worked on chitosan from grasshoppers and reported that male chitosan is more soluble in dilute acetic acid with about 75% solubility, while female chitosan has 46.34%.
3.6 GCMS characterization of chitosan from P. americana and A. domesticus
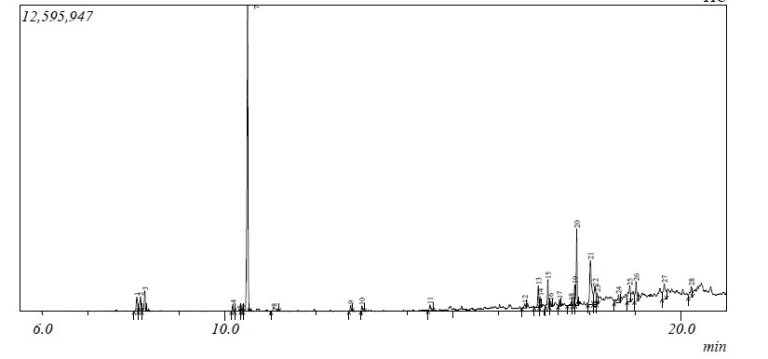
The GC-MS analysis carried out on the cricket chitosan (Table 3) revealed the presence of a total of 18 compounds (Table 3). The chromatogram of cricket chitosan is shown in Figure 4. The compounds identified include: cyclohexane,dimethylacetal, cyclohexane,1,5-diisopropyl-2,3-dimethyl, 3,7,11,15-Tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-ol, Pentadecanoic acid,14-methyl-methylester, Palmitic acid, linolelacidic,methylester 11-octadecanoic acid,methylester, stearic acid,methylester, oleic acid, octadecanoic acid, 2-piperidinone,N-[4-bromo-n-butyl]-palmitin,1,2-di,-2-aminoethylhydrogen phospha, 1-dodecanol,3,7,11-trimethyl, eicosanoic acid methyl ester, 9-octadecenal, oxalic acid, hexadecylhexyl ester, 2-methyl-Z, Z-3,13-Octadecadienol and linoleoyl chloride.
The various bioactive components present in the chitosan obtained from cockroach are shown in Table 4 and observed in Figure 5. A total of 17 compounds including cyclohexane, dimethyl acetal, pentadecanoic acid, 14-methyl-,methyl ester, hexadecanoic acid, 7-methyl-Z-tetradecen-1-ol acetate, linolelaidic acid, methyl ester, 11-octadecenoic acid, methyl ester, stearic acid methyl ester, oleic acid, octadecanoic acid, hexadecanohydrazide, decyl fluoride, arachic acid, octadecenylaldehyde, oxalic acid, 13-docosenoic acid, hexadecanoic acid,2,,3-dihydroxypropyl ester, linoleoyl chloride were identified
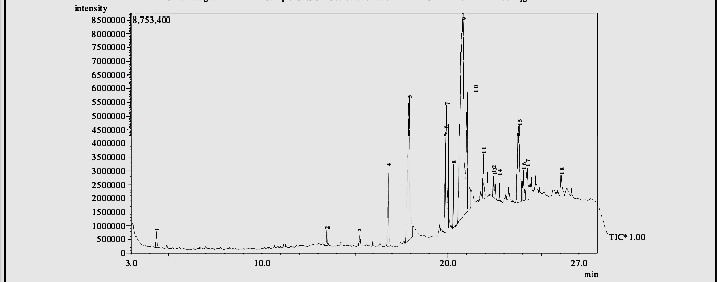
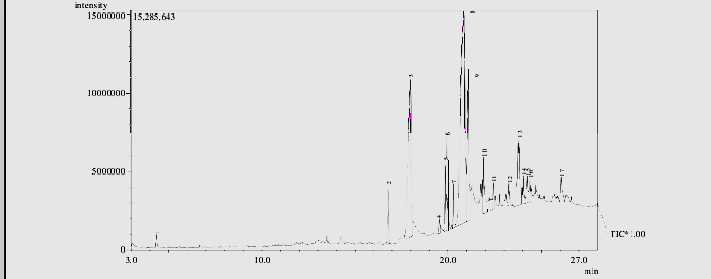
Table 3: Bioactive components of identified from cricket (Acheta domesticus) chitosan
| S/n | Retention Time | Area (%) | Base peak | Molecular weight (g/mol) | Molecular formular | Name of compound | Class of compound |
| 1. | 4.4 | 0.95 | 101.10 | 144 | C8H16 O | Cyclohexanone,dimethyl acetal | Benzene derivative |
| 2. | 13.5 | 0.59 | 97.23 | 196 | C14H28 | Cyclohexane,1,5-diisopropyl-2,3-dimethyl | Alkene derivative |
| 3. | 15.2 | 0.63 | 43.11 | 296 | C20H40O | 3,7,11,15-Tetra methyl-2-hexadecen-1-ol | Bicyclo derivative |
| 4. | 16.8 | 4.17 | 79.29 | 270 | C17H34O2 | Pentadecanoic acid,14-methyl-methyl ester | Bicyclo alcohol derivative |
| 5. | 17.9 | 16.68 | 43.18 | 256 | C16H32O2 | Palmitic acid | Multiple cyclic compound |
| 6. | 19.8 | 4.29 | 67.14 | 294 | C19H34O2 | Linolelaidic acid, methyl ester | Saturated tricyclo derivative |
| 7. | 19.9 | 5.22 | 55.22 | 296 | C19H36O2 | 11-Octadecenoic acid, methyl ester | Benzene derivative |
| 8 | 20.3 | 2.29 | 74.15 | 298 | C19H38O2 | Stearic acid, methyl ester | Unsaturated bicyclo derivative |
| 9 | 20.8 | 36.68 | 41.50 | 282 | C18H34O2 | Oleic acid | Chloro alkane derivative |
| 10 | 21.0 | 9.78 | 43.23 | 284 | C18H36O2 | Octadecanoic acid or stearic acid | Saturated fatty acid |
| 11 | 21.9 | 2.08 | 43.27 | 233 | C9H16Br NO | 2-Pieperidinone,N-[4-bromo-n-butyl] | Alkane derivative |
| 12 | 22.4 | 0.91 | 43.10 | 691 | C37H74NO8P | Palmitin,1,2-di,-2-aminoethyl hydrogen | Un saturated alcohol derivative |
| 13 | 22.5 | 1.01 | 55.39 | 228 | C15H32O | 1-dodecanol,3,7,11-trimethyl | Unsaturated alcohol derivative |
| ` | |||||||
| 14 | 22.7 | 0.64 | 74.10 | 326 | C21H42O2 | Eicosanoic acid, methyl ester | Fatty acid |
| 15 | 23.8 | 7.44 | 43.23 | 266 | C18H34O | 9-octadecenal or octa aldehyde | Alkane derivative |
| 16 | 24.0 | 1.77 | 43.10 | 398 | C24H46O4 | Oxalic acid, hexadecylhexylester | Saturated alcohol derivative |
| 17 | 24.2 | 3.00 | 55.79 | 280 | C19H36O | 2-Methyl-Z,Z-3,13-octadecadienol | Unsaturated alcohol derivative |
| 18 | 26.1 | 1.85 | 55.59 | 298 | C18H31ClO | Linoleoyl chloride | Unsaturated alcohol derivative |
Table 4: Bioactive components of identified from American cockroach (Periplaneta americana) chitosan
| S/n | Retention Time | Area (%) | Base peak | M.W (g/mol) | M.F | Compound Names | Class of compound |
| 1. | 4.4 | 0.68 | 105.05 | 120 | C9H12 | 0-Ethylmethylbenzene | Benzene derivative |
| 2. | 16.8 | 2.48 | 105.05 | 120 | C9H12 | 1-Hepten-5-yne, 2-methyl-3-methylene | Alkene derivative |
| 3. | 18.0 | 19.32 | 66.00 | 132 | C10H12 | Cyclobuta[1,2,3,4]dicyclopentene | Bicyclo derivative |
| 4. | 19.5 | 0.70 | 105.05 | 134 | C9H10O | 2-indanol | Bicyclo alcohol derivative |
| 5. | 19.9 | 2.43 | 66.00 | 134 | C10H14 | 3a,4,5,6,7,7a-Hexahydro-4,7-methanoindene | Multiple cyclic compound |
| 6. | 19.9 | 3.23 | 67.05 | 136 | C10H16 | Tricyclo[4.2.1.1(2,5)]decane | Saturated tricyclo derivative |
| 7. | 20.3 | 1.47 | 128.00 | 128 | C10H8 | 4-Phenylbut-3-ene-1-yne | Benzene derivative |
| 8 | 20.9 | 39.48 | 115.05 | 142 | C11H10 | 1,6-Methano[10]annulene | Unsaturated bicyclo derivative |
| 9 | 21.1 | 10.47 | 43.00 | 232 | C14H29 Cl | 1-Chloroteradecane | Chloro alkane derivative |
| 10 | 21.9 | 3.71 | 57.05 | 226 | C16H34 | 5-Propyltridecane | Alkane derivative |
| 11 | 22.4 | 2.17 | 57.05 | 268 | C19H40 | 2,6-Dimethylheptadecane | Alkane derivative |
| 12 | 23.3 | 1.25 | 43.00 | 250 | C18H34 | 1-Octadecyne | Un saturated alcohol derivative |
| 13 | 23.8 | 6.33 | 43.00 | 296 | C20H40O | 3,7,11,15-Tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-ol | Unsaturated alcohol derivative |
| ` | |||||||
| 14 | 24.0 | 1.09 | 43.00 | 256 | C16H32O2 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | Fatty acid |
| 15 | 24.2 | 2.05 | 43.00 | 170 | C12H26 | 3,4,5,6-tetramethyloctane | Alkane derivative |
| 16 | 24.4 | 1.24 | 43.00 | 186 | C12H26O, | 2-Butyloctanol | Saturated alcohol derivative |
| 17 | 26.1 | 1.90 | 71.05 | 296 | C20H40O | 3,7,11,15-Tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-ol | Unsaturated alcohol derivative |
The GCMS result of cockroach and cricket from this study, coincides with the study of Mahmoud et al. (2020) explored simplified methods for insect’s chitin extraction and obtained benzene derivative, fatty acid, alkene derivative, bicycle derivative, bicyclo alcohol derivative, unsaturated alcohol derivatives, chloro alkane and multiple cyclic compound. Takeshi et al. [32] carried out GCMS on chitin and chitosan from molluscan shells, they found out that chitosan contained fatty acid, alkane derivative, saturated alcohol, unsaturated alcohol, chloroalkane derivative which are also present in this present study.
Multiple cyclic compounds act by binding to chemicals on the membrane that surrounds the insect nerve cells which causes distortion in the membrane structure. Substances like the fatty acids also disrupts enzymes that the body of the insect uses to take up food and oxygen which cause the body of the insect to stop functioning. Unsaturated alcohol derivatives are known to cause repeated stimulations at the receptor site which result in multiple nerve impulses and seizures. Chloro alkane and unsaturated bicyclo derivatives work against insects nervous system by either blocking nerve impulses or by over stimulating them [33][34].
Benzene derivatives inhibits the function of the genetic makeup of bacteria there by killing the organism. [35]. The toxicity decreases with increase in the methyl substitution and in some cases it increases with increase in methyl substitution. GC-MS spectrum confirmed the presence of various components with different retention time as illustrated in figure 1 and 2. The mass spectrometer analyzes the compounds elucidated at different times to identify the nature and structure of the compounds. The large compound fragments in to small compounds giving rise to the appearance of peaks at different M/Z ratios the mass spectra are finger print of that compound which can be identified from the data library.
The present study helps to predict the formular and characterize 18 compounds in the chitosan from cricket and 17 compounds from the chitosan from cockroach. Further investigation may lead to isolation of bioactive compounds and their structural elucidation and screening of pharmacological activity will be helpful for further drug development.
4.0 Conclusion
This study reveals that chitin and chitosan can be extracted from cockroach and cricket. The presence of various bioactive compounds detected after GC-MS analysis using the chitosan from cricket and cockroach justifies the use of the chitosan for various uses like bio medical, cosmetic and waste water management. However, isolation of individual phytochemical constituents and subjecting it to biological activity will be definitely giving fruitful results and will open a new area of investigation of individual components and their pharmacological potency. From these results it could be concluded that chitosan from cricket and cockroach contains various bioactive compounds. Evaluation of pharmacological activity is under progress. Therefore, it is recommended as insects of pharmaceutical importance
Acknowledgement: Authors are appreciative for the support from the Head, Department of microbiology and laboratory technicians for providing enabling environment and expertise for the accomplishment of this investigation.
Authors Contributions: The work was conducted in collaboration of all authors. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have no conflict of interest.
Funding: This research received no external funding”
Ethics Approval Statement: Not applicable
References
14. Stevens, C.V. Chitin and Chitosan: properties and applications. 2019.