Production and partial characterization of protease from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis isolated from domestic waste dumpsite
AROC in Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology, 2021,1(1);26-33
- Author(s): Tsado A. Ndarubu, Jiya A. Gboke, Ibrahim A. Habiba, Gana David, Zubairu Rakiya, Danazumi Nathaniel, Mohammed A. Saba, Aliyu Muhammad, and Akinniran C. Sunday
- July 22, 2021
- Keywords - Domestic waste, Partial characterization, protease Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
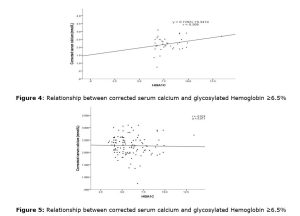
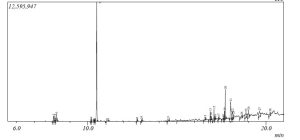
Background: Microorganisms are the leading source of industrial proteases. As a result of this, researchers are searching for new microbial strain with novel characteristic for protease production. Methods: In this study, some microbial strains were isolated from a soil sample obtained from domestic waste dumpsite. The isolate was screened for protease activity using casein as substrate. The proteolytic isolates were identified and used for protease production. The optimum pH and temperature as well as kinetic parameters of the enzyme were determined to predict their suitable industrial applications. Results: Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis were identified to be active proteases producers. The optimum temperature of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis were both recorded at 50OC while the optimum pH of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis were recorded at 8.0 and 9.0 respectively. The Km and Vmax of protease produced from Pseudomonas aeruginosa were 222.22U/ml and 0.625mg/ml respectively while the Km and Vmax were proteases produced from Bacillus subtilis were 135.13 U/ml and 0.402 mg/ml respectively. Conclusion: The results in this study suggest that domestic waste dumpsite could be a potential source of proteolytic isolates of novel characteristic.
Corresponding Author(s)
Tsado A. Ndarubu
Email: infoamosndarubu@gmail.com
Mobile-+2348032920909
Citations
Tsado A. N., Jiya, A.G., Ibrahim, A.H., Gana, D., Zubairu, R., Danazumi, N., Mohammed, A.S., Aliyu, M., and Akinniran, C.S. (2021). Production and partial characterization of protease from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis isolated from domestic waste dumpsite. AROC in Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology, 01(01);26-33